Arduino is an amazing tool for physical computing — it’s an open source
microcontroller board, plus a free software development environment. Use it to make cool interactive objects that can sense inputs from switches, sensors, and computers — and then control motors, lights, and other physical outputs in the real world.
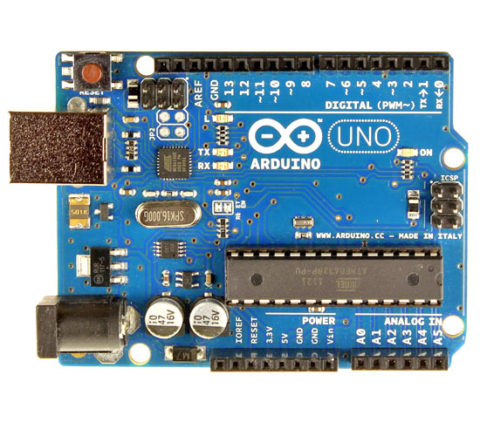
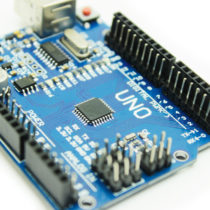
The Uno is compatible with all current shields and code, and comes assembled — simply connect it to a computer with a USB cable or power it with an AC-to-DC adapter or battery.
The Arduino Uno board is based on the ATmega328 (datasheet). It has 14 digital input/output pins (of which 6 can be used as PWM outputs), 6 analog inputs, a 16 MHz ceramic resonator, a USB connection, a power jack, an ICSP header, and a reset button. It contains everything needed to support the microcontroller; simply connect it to a computer with a USB cable or power it with an AC-to-DC adapter or battery to get started. The Uno differs from all preceding boards in that it does not use the FTDI USB-to-serial driver chip. Instead, it features the Atmega16U2 (Atmega8U2 up to version R2) programmed as a USB-to-serial converter.
Features:
- Microcontroller ATmega328
- Operating Voltage : 5V
- Input Voltage (recommended) : 7-12V
- Input Voltage (limits) : 6-20V
- Digital I/O Pins :14 (6 of which provide PWM output)
- Analog Input Pins 6
- DC Current per I/O Pin 40 mA
- DC Current for 3.3V Pin 50 mA
- Flash Memory 32 KB (ATmega328) of which 0.5 KB used by bootloader
- SRAM 2 KB (ATmega328)
- EEPROM 1 KB (ATmega328)
- Clock Speed 16 MHz